The Archives Unleashed Cloud
The Archives Unleashed Cloud is Closed
The Cloud shut down on 30 June 2021, and will be replaced by a similar service hosted by Archive-It. Learn more about the transition here.

Introduction
The Archives Unleashed Cloud was an open-source cloud-based analysis tool that helps researchers and scholars conduct web archive analysis. It supported the priorities of accessibility and usability of web archives by providing users with a web-based front end to access the Archives Unleashed Toolkit. It was primarily developed by our project co-investigator and developer, Nick Ruest.
Lessons learned from the project are informing our new integrated service with Archive-It.
Functionalities
The Cloud had a clean and easy-to-use modern interface. The best part is that you did not need to know how to code, supporting the increased accessibility of working with web archives.
Core features of the Archives Unleashed Cloud included:
- Syncing Archive-It collections;
- Ingesting Archive-It collections via WASAPI to the Cloud;
- Creating a network graph, domain distribution list, full text, and full text by domain derivatives, and making each available for download;
- Providing in-browser diagrams to highlight a collection’s crawl frequency, interactive network graph (to see major nodes and connections within your collection), and domains graph.
Following Content is Archived
The following content refers to the now closed Archives Unleashed Cloud. We are keeping it here as a record of the project.
A Guided Tour of the Archives Unleashed Cloud
Let’s take a tour of how the Cloud works. Below you will find a video tour of the Archives Unleashed Cloud, followed by a brief overview of what you can expect when working with the platform.
Once a user signs up to the Archives Unleashed Cloud, they enter their Archive-It credentials, which are salted and encrypted. Those credentials are then used to sync their Archive-It collections with the Cloud using Archive-It’s WASAPI endpoint. This is done as a background job, and once it is complete, it emails the user to let them know that their Archive-It collections are synced and available for further analysis.
The main collections screen provides some basic information about each collection: title, if the collection has been analyzed in the Cloud yet, if it is publicly available (in Archive-It), the number of ARC/WARCs in the collection, and the size of the collection. You can see this below!
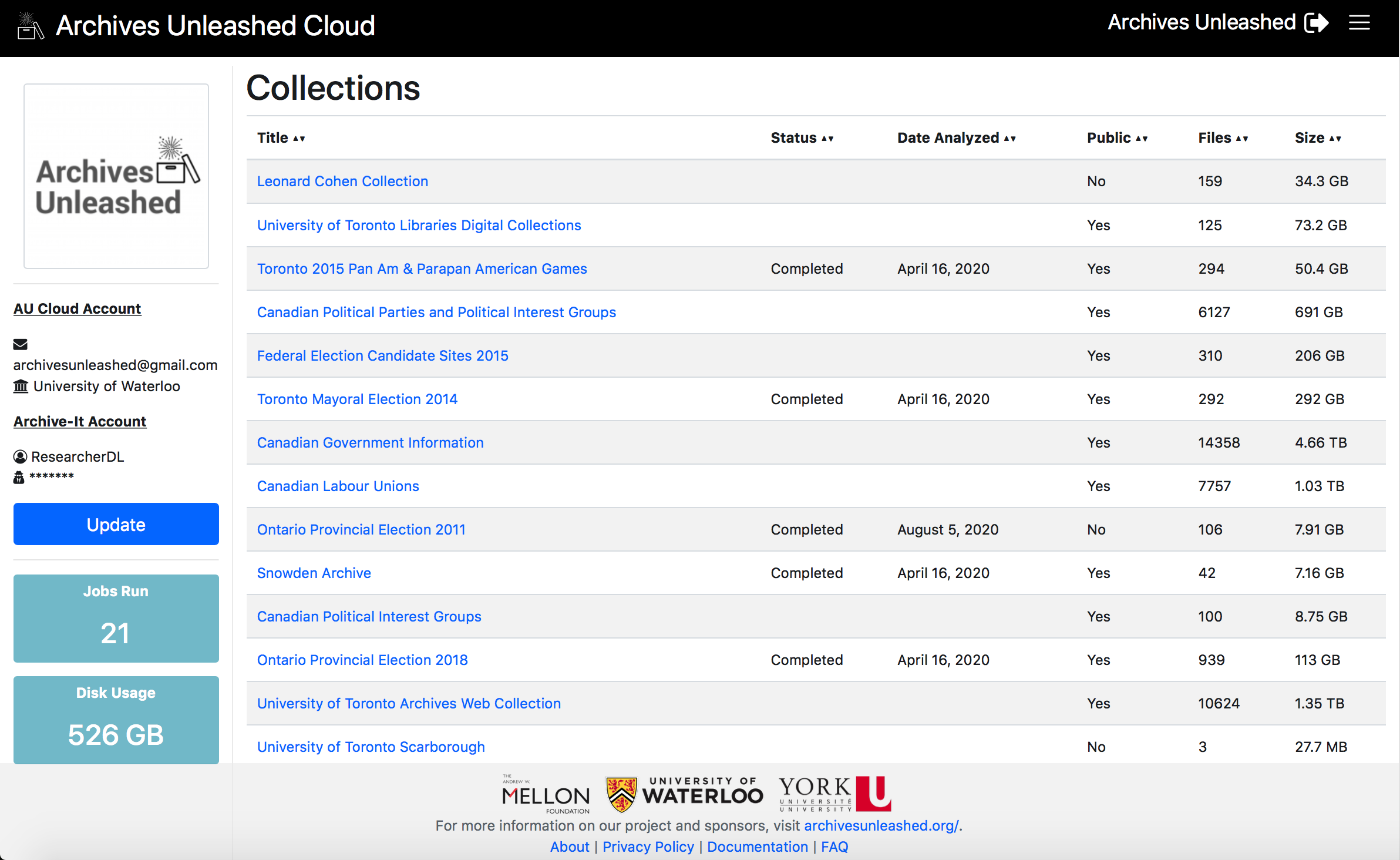
From the main collections screen, users can select a specific collection to download, which will trigger a number of background jobs. The first job uses data gathered from the WASAPI endpoint to download and verify each ARC/WARC file to our Archives Unleashed Cloud instance. Once the entire collection is downloaded, an automatic email is generated to notify the user that the collection has been downloaded, and analysis will begin.
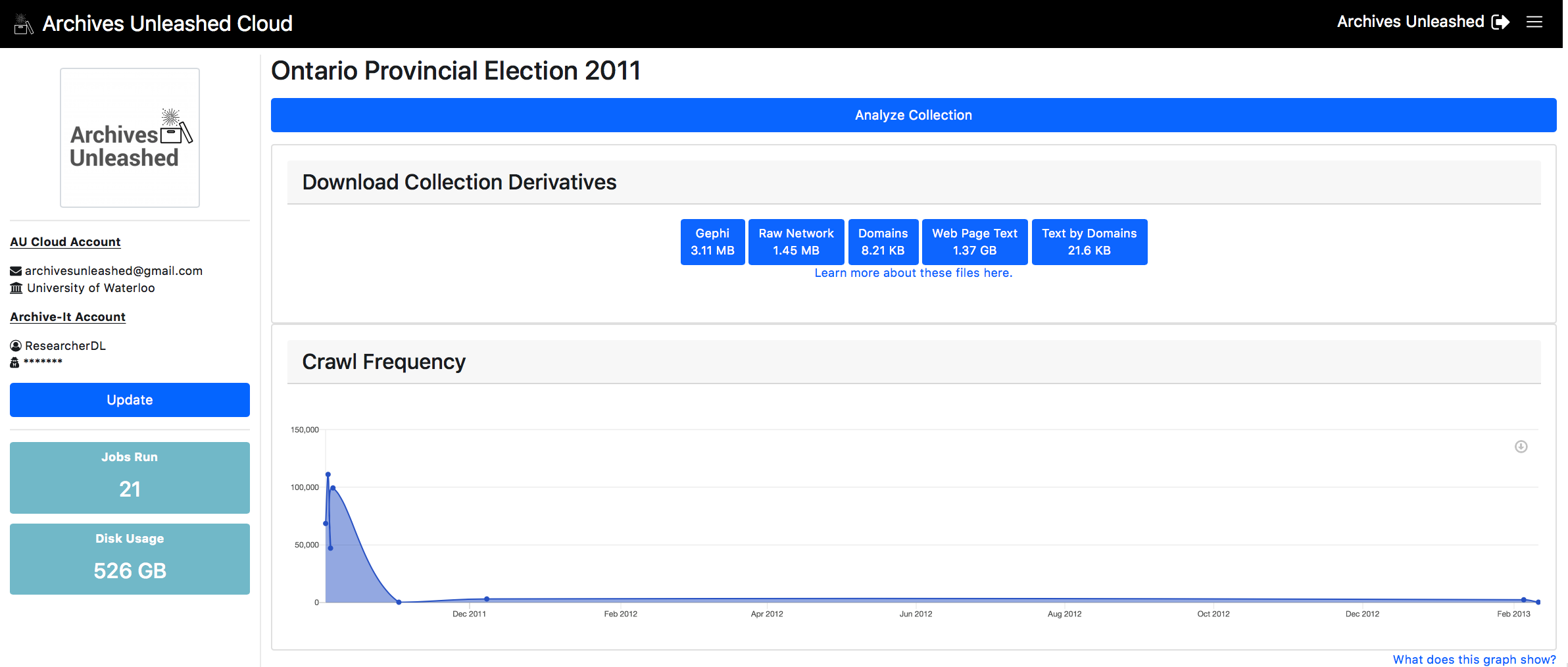
The analysis process then triggers an Apache Spark job and uses AUT to create a basic set of derivatives:
- A GEXF file which you can load with Gephi. It has a basic layout courtesy of our GraphPass program, which allows you to see major nodes and communities in the network;
- A GraphML file which you can load with Gephi. It does not have any basic layouts or transformations, requiring you to do so manually. You can use GraphPass to provide layout if you wish to add that feature to your file;
- A CSV file that explains the distribution of domains within the web archive;
- A CSV file that contains the text extracted from HTML documents within the web archive. You can find the crawl date, full URL, and the plain text of each page within the file;
- A ZIP file that contains the plain text extracted from HTML documents within the web archive, arranged by each domain. Within this ZIP you will have a series of text files, each containing the full text of a top-ten domain.
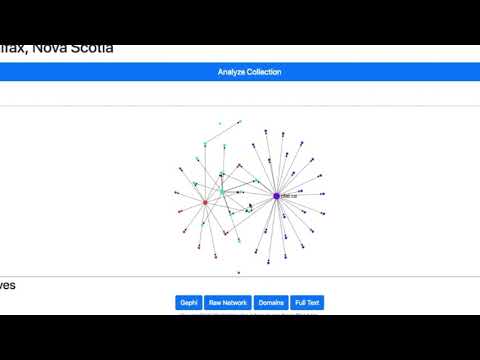
Here is a completed collection page:
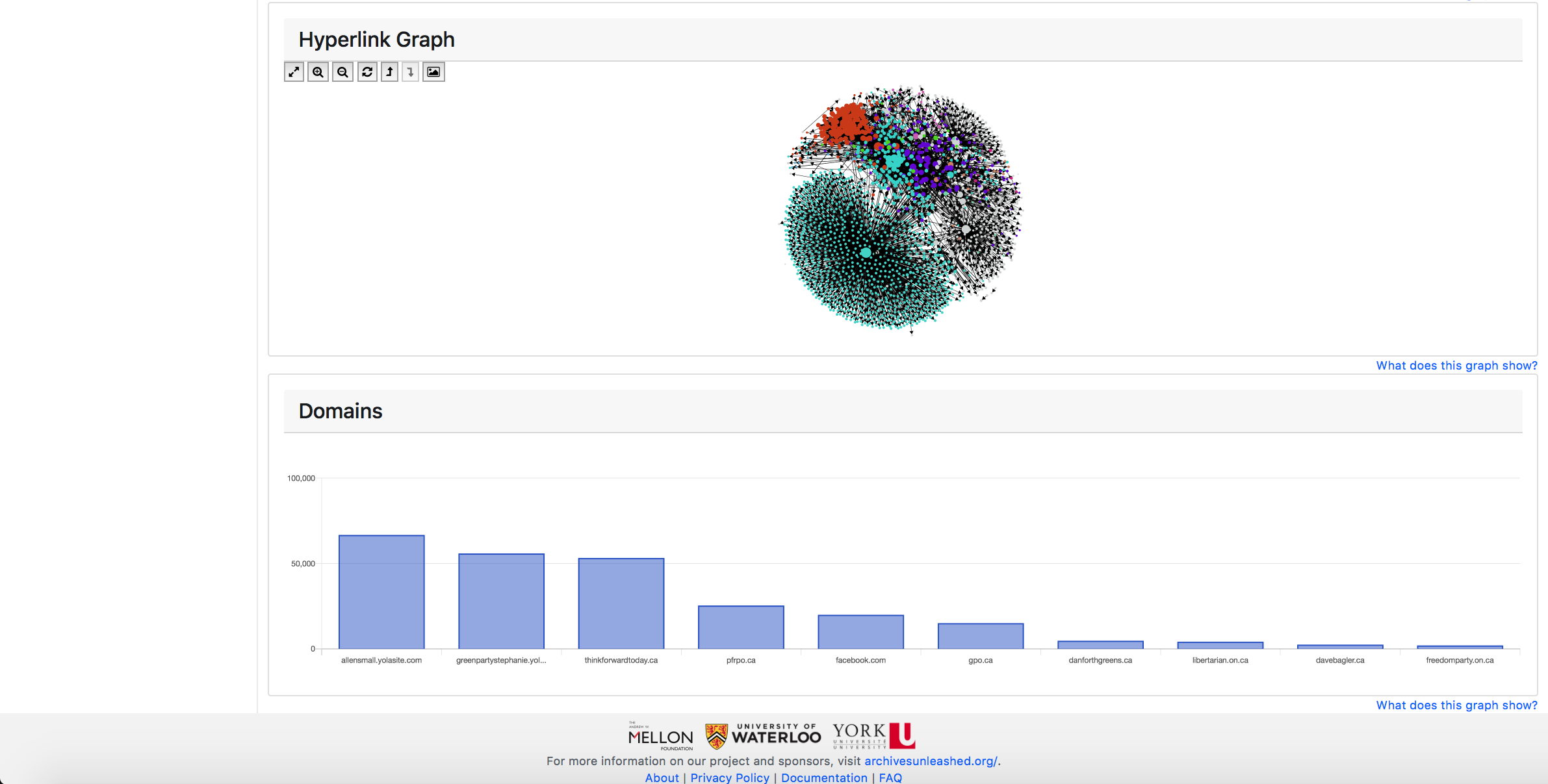
In addition, we use GraphPass to help to create a simple network visualization powered by Sigma js on the collection page. Sigma is a JavaScript library that assists in drawing and displaying graphs.
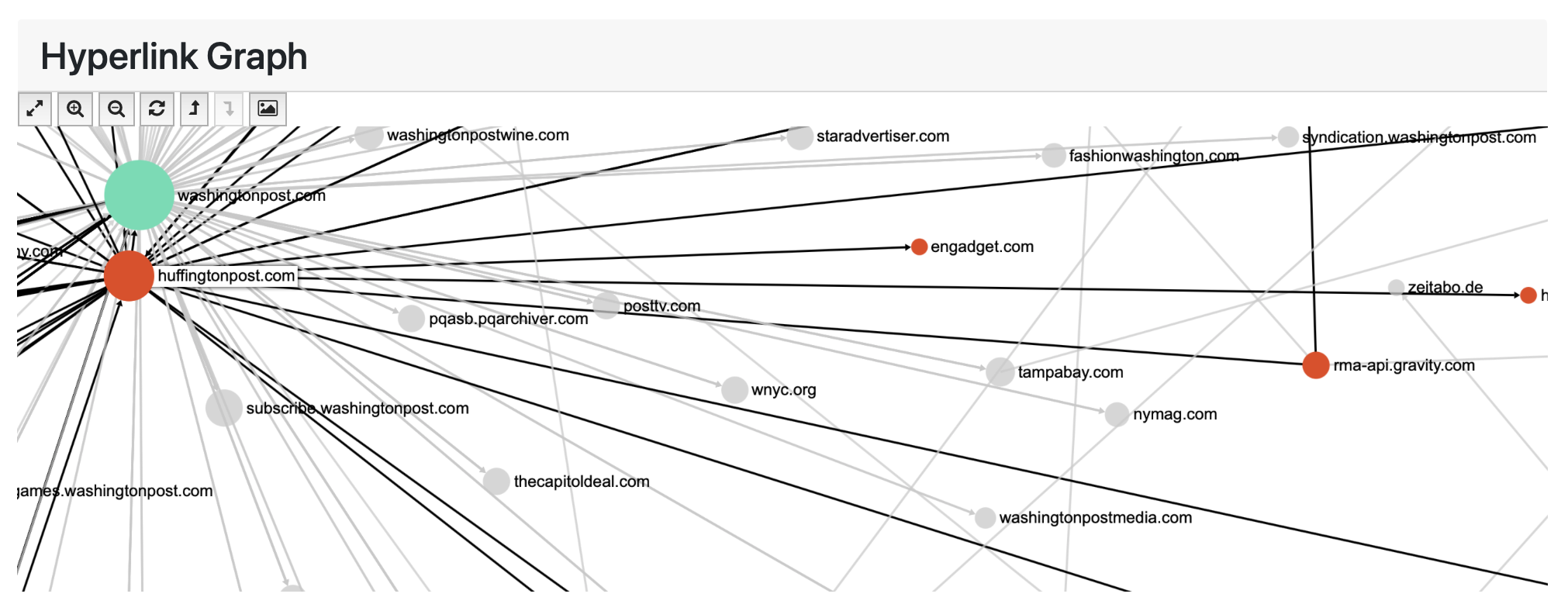
GraphPass produces visualization-related data in the network files such as colour, position and size based on common social network algorithms. In the networks, each node (dot) represents a domain (i.e. all of the URLs within a domain such as “yorku.ca” or “newyorktimes.com”) and each edge (line) represents a link from one node to another.
Users can explore and interact with the network using the helper buttons in the top left corner of the network window.
- Full Screen - opens up the network to full screen for easier interaction
- Zoom in/out - zooms the camera into the network and away from it
- Refresh - brings the network diagram back to its original state
- Scale up and scale down - allows users to see more or less node labels in the network

A few cautionary notes on “scale up” and “scale down” are in order. With website networks, some sites have so many links compared to the others, that they obscure everything else. The Archives Unleashed Cloud’s scale-up feature uses logarithmic transformation to make the graph a bit easier to read. For example, six nodes with size values 1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000 and 1,000,000,000 can be transformed using a base 10 logarithm to produce new sizes 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, & 9, making the node sizes much closer together in size.
A logarithm is a mathematical expression used to deal with non-normal distributed data (like networks). It is created by giving a base number an exponent, which is then multiplied by itself, to create factor increments, rather than equal amount increments, between data points. This is important as it will allow for data points to be more evenly distributed with minimal influence on data accuracy and integrity.
You can further interact with the hyperlink diagram by hovering over any node to highlight its immediate connections to other nodes. The arrow on each line indicates the direction of connection, for instance, in the image below, we see an arrow connecting two nodes and reveals that huffingtonpost.com has a link to the engadget.com domain.
Future development will focus on filtering further down on a collection, and integrating the new DataFrame functionality we’re adding to AUT via a JDBC connector.
Can I try it out?
The Archives Unleashed Cloud is an open-source project; you can view the codebase here. Although it is tied closely to the canonical instance running at http://cloud.archivesunleashed.org, it can also be run as a standalone project on your own server, desktop, or laptop! That said, our primary focus is on the canonical instance that we are hosting. However, if there is interest in generalizing aspects of the project, let us know and we can collaborate and figure out how to make it happen.
Citing Archives Unleashed
Your citations help to further the recognition of using open-source tools for scientific inquiry, assists in growing the web archiving community, and acknowledges the efforts of contributors to this project.
How to cite the Archives Unleashed Toolkit or Cloud in your research:
| Nick Ruest, Jimmy Lin, Ian Milligan, and Samantha Fritz. 2020. The Archives Unleashed Project: Technology, Process, and Community to Improve Scholarly Access to Web Archives. In Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE Joint Conference on Digital Libraries in 2020 (JCDL ‘20). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 157–166. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3383583.3398513 |